Magnetic Particle Inspection Aircraft - The first commercial Boeing airplane structures were visually inspected during manufacturing to verify proper wood frame assembly, fabric attachment and adhesive application during fabrication. No instruments beyond the human eye were used, except possibly lighting aids or magnification to improve defect detectability.
The value of utilizing NDE and other measurement data as a process control tool is only now being fully appreciated. The goal is to move inspection (such as UT, IRT, CT, etc.) back up the manufacturing chain so it becomes transparent to the fabrication process.
Magnetic Particle Inspection Aircraft

This approach will drive quality improvements through trend analysis, and reductions in process variations. In-process sensor feedback during manufacturing will be expanded to newer manufacturing methods, like additive manufacturing. The testing method is based on the principle that magnetic flux in a magnetized object is locally distorted by the presence of discontinuity.
Fatigue Type Defects
This distortion causes some of the magnetic field to exit & re-enter the test object at the discontinuity. This phenomenon is called magnetic flux leakage. Flux leakage is capable of attracting finely divided particles of magnetic materials that in turn form an 'indication' of the discontinuity.
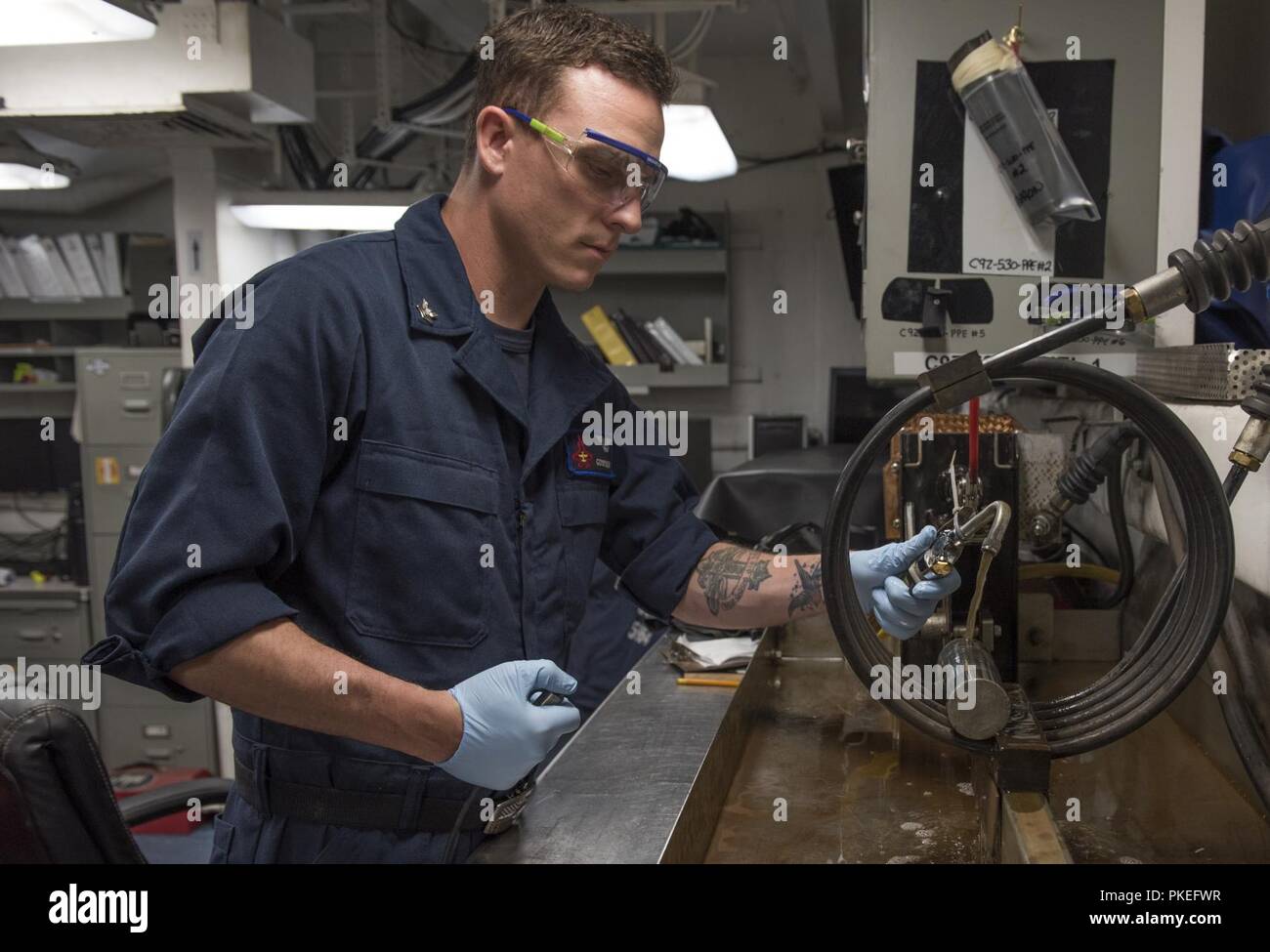
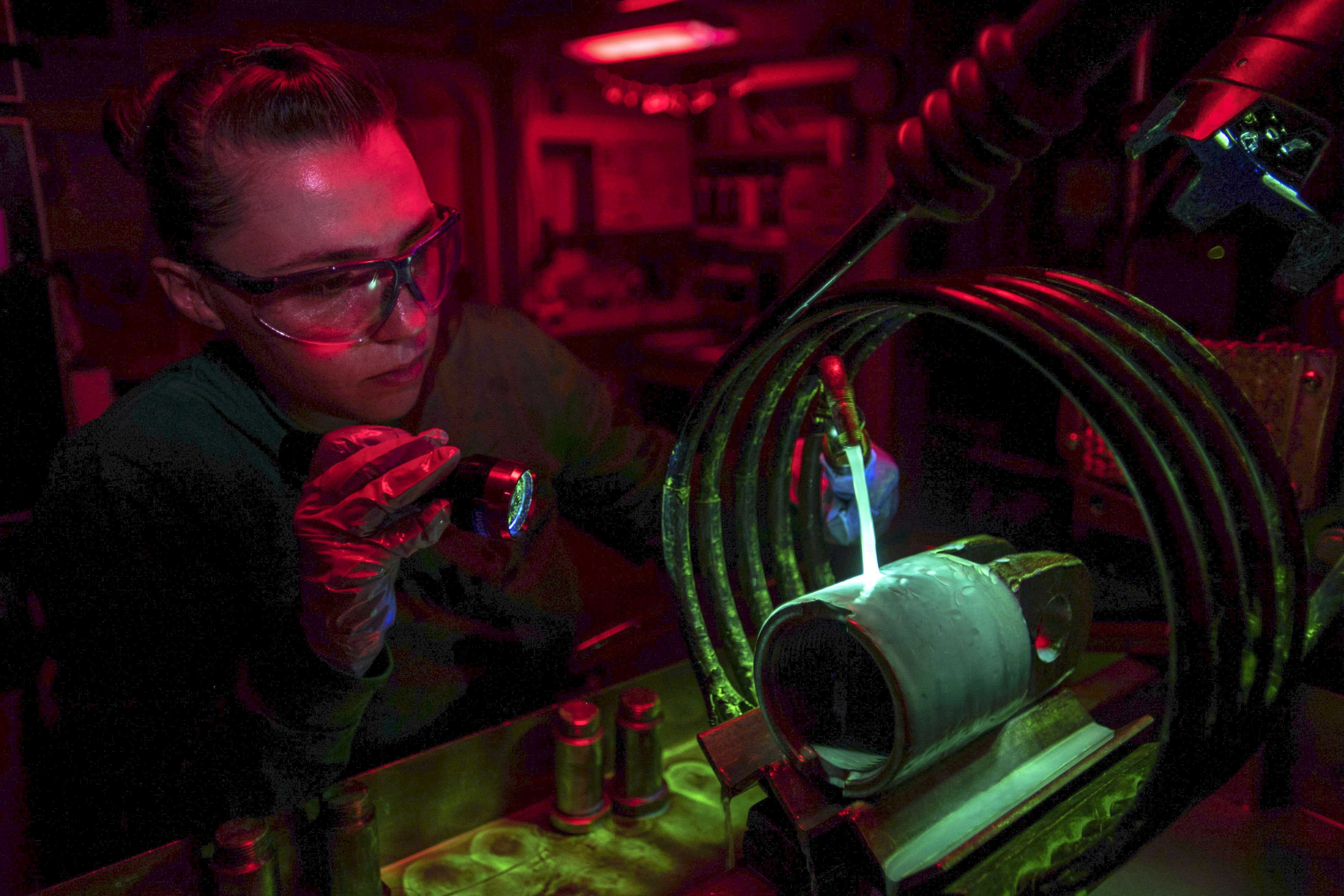
Therefore, the test basically consists of three operations: a) Establish a suitable magnetic flux in the test object by circular or longitudinal magnetisation. b) Apply magnetic particles in dry powder of a liquid suspension; and c) Examine the test object under suitable lighting conditions for interpreting & evaluating the indications.
Applications : Considering the penetration and absorption capability of x-radiation, radiography is used to inspect a variety of nonmetallic parts; for porosity, water entrapment, crushed core, cracks and resin rich/starved conditions; and metallic products; such as welds, castings and forging as well as locating discontinuities in fabricated structural assemblies such as cracks, corrosion, inclusions, debris, loose fittings, rivets, out of round holes & thickness variations.
Gamma ray radiography is usually used for detection of internal flaws of aircraft structure (steel & titanium) and engine components which require higher energy levels or other assemblies where access is difficult. World War II saw the development of the first eddy current instruments, as well as the first ultrasonic testing method.
Other Crack Detection Methods
These became the crux of aerospace NDE as Boeing entered the jet age in the mid-1950s. As the space program came along in the 1960s, McDonnell had a hand in the development of the first Sondicator to support inspection of heat shield bonds on the Gemini spacecraft, probably the most critical element of the vehicle.
The early Sondicator led to the development of more advanced low-frequency bond testing methods still used today for inspection of adhesive bonds. Solvents, in general, have a defatting action and are therefore harmful to the skin.

They may produce dermatitis in the long term unless skin contact is minimized. They are generally relatively volatile, giving off vapors that can be inhaled. The health effects depend on the exposure and the relative toxicity of the solvent.
These may include irritation of the eyes and lungs, headache, nausea, dizziness and light-headedness. Unconsciousness or even death can result from exposure to high levels of solvent vapors. Standard methods require a specific range of values for the tangential component of the magnetic induction or for the magnetic field strength near the surface of a test piece.
Standard Methods
From 3200 A/m (40 Oe) to 1600 A/m (20 Oe) is required in the International Standardization Organization, ISO[2]. Det Nork Veritas [3], DNV, require from 4000 A/m (50 Oe) to 2400 A/m (30 Oe) and Petróleo Brasileiro[4], PETROBRÁS, require from 6500 A/m (81.6 Oe) to 1700 A
/m (21.4 Oe). Compatibility with the instrument & material selection different types of probes are used Such are i) High frequency surface & bolt hole probes ii) High frequency special probes (counter sink plug & shaped) iii) Low frequency probe (spot encircling & shaped) iv)
Sliding probe (driver/receiver). Several major air catastrophes drove the need for better NDE. The F-111 crashes of the late 1960s and early 1970s led to the introduction of the fail-safe/damage-tolerant design philosophy. The first aircraft designed in the damage tolerance era was the Boeing (McDonnell Douglas) F-15.
Boeing, along with Pratt & Whitney from the engine side, took the lead in addressing inspection reliability in conjunction with all NDE processes used to support manufacturing. Because of the need to rely in the future too on a sensitive but cheap technique for billions of parts per year (e.g. in automotive industry) a new concept of MPI was developed and will be presented here:
Magnetic Particle
These fatigue cracks, and cracks generated by excessive loads or corrosion could be identified using an NDE method called dye penetrant, which relies on a dye wicking into surface cracks. Structural parts made with most steels could be inspected with magnetic particle inspection.
Both these methods essentially enhance visual inspection. Visual inspections require human reckoning that requires high skill interpretation and judgment. As the need for inspection increased, new instrumented methods had to be developed to allow discovery with less judgement.
The intensity and frequency/wavelength of the radiation can be correlated closely with the heat of the radiator. it follows that radiation sensors can be used to tell us about the physical condition of the test object.
This is the basis of the technology of 'thermography'. Boeing has been a world leader in the development of automated ultrasonic scanning systems, for production and in-service inspection of composite structures. Two examples of Boeing Automated Ultrasonic Scanning System (AUSS) options are shown in Figures 5a and 5b.
Radiation Methods X-Rays Neutrons Isotope Sources
Resonance testing instruments may operate either or both in the sonic or ultrasonic frequency range. Different methods of transmitting and receiving energy have been developed. Basically, each technique introduces a pressure wave into the specimen and then detects the resonant, transmitted or reflected wave.
Applications: Eddy current test is used to detect surface & subsurface defects, corrosion in aircraft structures, fastener holes and bolt holes. Surface detects and conductivity testing by high frequency and sub-surface detects by low frequency methods.
Fluorescent or black oxide particles in the aerosol cans are used during critical areas of aircraft structure/components inspection when using either permanent or electromagnets. Fluorescent particle inspection method is evaluated by black light (Black light consists of a 100 watt mercury vapor projection spot lamp equipped with a filter to transmit wave length between 3200 to 3800 Angstrom unit and absorb substantially all visible white light).
X-ray Backscatter does not require access to both sides of a structure in order to do an inspection, which is an advantage for NDE of both large and in-service structures. It also selectively scatters from and discriminates between materials.
Traditional Resultant Magnetizing Method
The method is particularly sensitive to adhesives, moisture ingress, density changes, voids, and foreign object debris. It has recently been shown to be able to characterize composite heat damage and detect wrinkles in composites. More research is needed to quantify these new capabilities.
Bulk supplies of solvents or aerosols should be stored separately from the work room, in containers appropriate for their properties, e.g. highly flammable substances, and preparations should be stored in metal cabinets, clearly labeled to indicate the nature of the contents.

Only the quantity required for immediate work should be kept in the work room. Early detection of cracks will allow trend monitoring. The rate of crack propagation analysis can be used in estimating the residual life expectancy.
Unfortunately, the probability of finding cracks of the length of 3 mm is only 75% and those of 5 mm 85%. The chances of finding those even smaller will be very much less. If the operating environment is conducive to cracks then there is always a 15% chance that an undetected crack is present.
In these situations it may well be prudent to estimate the residual life for a 5 mm crack and ensure that the prescribed period before inspection is less. Standards were established in the early to mid-1990s for aerospace components and the resulting reports are still referenced today.
CT provides 2D and 3D imaging of material density, voids, porosity and geometry with very high resolution capability for smaller parts. Today, CT is a key technology in supporting qualification and certification of metallic parts fabricated using additive manufacturing processes.
The fundamental purpose of penetrant testing is to increase the visible contrast between a discontinuity & its background. This is achieved by treating the area with an appropriately formulated liquid of high mobility & penetrating power (which enters the surface cavities),
and then encouraging the liquid to emerge from the developer, to reveal the flaw pattern under white light (when visible dye penetrants are used) or under ultraviolet light (when fluorescent penetrants are used). Evaluation also conducted with the aid of 3X to 5X magnification.
The objective of liquid penetrant testing is to provide visual evidence cracks, porosity, laps, seams of other surface discontinuities rapidly & economically with a high degree of reliability. vi) Video Imagescope - The video Imagescope is similar to a Fibrescope with the exception that a video camera and its connections have replaced the image bundle and a TV monitor has replaced the eyepiece.
This image may be magnified for precise viewing. The field of vision is up to 90 degrees and the probe tip has four way articulation. Presently the smallest diameter is 9.5 mm with working length up to 100 feet.

Visual inspection was exclusively used in the early years of aircraft up to the early 1930s, when the first all metal airplane, the Boeing Model 247, was introduced. Industrial radiographic inspection processes for metals and the first magnetic induction/magnetic particle inspection approach were introduced in the 1920s.
These were applied on a limited basis for inspection of Model 247 components, as well as the more mass-produced Douglas DC-3 that came along in 1936. iii) Microscope - It is a multiple element magnifier, providing very high power magnification, is used for the inspection of parts removed from the aircraft.
Some portable units are also used to evaluate suspected indications found on the aircraft. NDE can generally be defined as the evaluation of a structure without harming or affecting its purpose. This definition sets NDE apart from destructive or mechanical testing of subscale or full-scale structures, which allows the determination of properties or flaws, but which makes the part unusable afterwards.
NDE for aerospace covers two distinct but related application areas: NDE during production and NDE during in-service usage. There arises from time to time in the use of MPI a situation which at first appears very mysterious.
One component may be tested in one place and a number of indications recorded and then tested at another and the indications initially recorded are absent but others found. If, after preliminary checks of techniques such as magnetic ink strength, time of magnetisation etc.
the problem remains it is usually due to the fact that one test was carried out using alternating current magnetisation and the other some form of rectified current. Gamma-ray : Gamma-rays are the emissions from the disintegrating nuclei of radioactive substances.
Two most commonly used 'isotopes' for performing industrial inspections are Iridium-192 and Cobalt-60. But in aircraft maintenance during gamma-radiography Iridium-192 is usually used. Isotopes of Radium-226 and Cesium-13 7 are available but are not generally used for aircraft radiography.
Gamma-ray radiography has the advantages of simplicity of apparatus, compactness of the radioactive sources and independence from external electrical sources. An electric current-based method developed first in the industries making and inspecting pipes and tubes. It was the first significantly used instrumented method of NDE in aerospace.

With this method, a changing electromagnetic field is generated by a coil containing alternating or pulsed electric current. The field produces corresponding electric (eddy) currents in the metal, whose paths are modified by cracks. The same coil or a separate receiving coil senses the field change that the eddy currents produce, thereby allowing detection of cracks using electronic circuitry and (first) analog then (later) digital display.
Applications: Simple in principle, easily portable. Fast and effective for surface & subsurface defects in ferromagnetic materials of any shape, removed from engines, pumps, landing gear, gear boxes, shafts, shock struts etc. Widely used for bolt inspection.
While visual inspection continued to be the primary NDE method, visual inspection could no longer address the defect and damage detection needs, especially in-service. Metal fatigue caused by the cyclic stresses of aircraft flight produces small cracks that must be identified before they grow to the point of structural failure.
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction DIFFERENT NDT METHODS Liquid Penetrant Magnetic Particle Eddy Current Ultrasonic Radiography Visual/Optical Sonic / Resonance Infrared Thermography Conclusion References CGM CIGIEMME S.p.A. designs and manufactures a complete range of Magnetic Testing (MT) and Penetrant Testing (PT) systems, from simple equipment to highly customized systems, also offering a complete range of consumables, tools, accessories and instruments used in the MT and PT fields.
Eddy currents are electrical currents induced in a conductor of electricity by reaction with an alternating magnetic field. Eddy currents are circular & oriented perpendicular to the direction of the applied magnetic field. The a) electrical conductivity b) magnetic permeability c) geometry and d) homogeneity of the test object, all affect the induced currents.
Structures & different assemblies of aircraft are made from various materials, such as aluminum alloy, steel, titanium and composite materials. To dismantle the aircraft in pieces and then examine each component would take a long time, so the NDT method and equipment selection must be fast and effective.
Key Points: Fast & simple to use, inexpensive and easily transportable. Can detect very small surface discontinuity. Can be used on aircraft or in the workshop. Frequently used to confirm suspected defects. Area to be cleaned before and after check.
magnetic particle inspection specification, magnetic particle inspection video, magnetic particle inspection near me, magnetic particle inspection training, magnetic particle inspection equipment, magnetic particle inspection supplies, magnetic particle inspection kit, magnetic particle inspection practice test








/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/tgam/PJ6DLXNUCRD6BC45ZYNIIDGSGY)